How Do Autoclaves Sterilize Medical Devices?
What is considered sterile for sterilization validation?
Under the strictest definition of sterility, an item or product is sterile when there is a complete absence of viable microorganisms (bacteria, yeasts, viruses, and molds). For regulatory purposes, sterility is defined by acceptance criteria based on calculated contamination probability. An acceptable level of contamination risk for most items is the probability of contamination for one in a million products. However, sterility criteria may be more stringent or lax depending upon the intended use of the medical device or product.
What are sterilization validations, and why are they important?
Since the sterility of a medical device or product is based on acceptance criteria, the process that a product or device undergoes to become sterile must be validated to prove that sterility acceptance criteria are consistently met. Sterility can be assured only using a validated sterilization process under current good manufacturing practices (cGMP). Sterility cannot be demonstrated by reliance on periodic sterility testing of final products alone. Thus, sterilization validations are tests that accumulate data about a sterilization process and statistically prove that the sterilization process can consistently sterilize medical devices or products under “worst-case scenario” conditions. For steam sterilization, the overkill method is used for sterilization validations.
What is steam sterilization (moist heat sterilization)?
Sterilization by moist heat (also known as steam sterilization) destroys microorganisms in a product with pressurized steam. Sterilization by moist heat is the most common method for medical device and medical product sterilization. However, autoclaves cannot sterilize medical devices with heat and humidity-sensitive materials.
What is an autoclave?
An autoclave is a programmable steam sterilization chamber that uses a combination of pressure and steam to sterilize medical devices and other items. As steam sterilization is one of the most common sterilization processes, autoclaves are found everywhere, from medical practitioner’s offices to large-scale manufacturing facilities.

What items can be steam sterilized in an autoclave?
Items traditionally sterilized by moist heat include durable plastic materials, glass items, metal items (mixing tanks), surgical equipment, filling equipment, ceramic items, elastomeric materials (such as rubber), freeze-dryer chambers, and filled product containers that can withstand thermal degradation at high temperatures. Often, medical devices are wrapped in cloth when sterilized to maintain their sterility outside of the autoclave until use.
How do autoclaves sterilize medical devices?
As mentioned earlier, autoclaves operate through saturated steam sterilization. Saturated steam is heated water in a balance between its gas and liquid phases. As steam requires both a water’s gaseous and liquid phases, steam is known as a biphasic mixture. The balance of water’s gas and liquid phases for saturated steam is regulated by temperature and pressure. There is only one pressure at which steam will saturate for any one temperature. Saturated steam kills microorganisms with the liquid water phase of the saturated steam. Thus, steam that is heated above saturation (known as superheated steam) will be less lethal to microbes despite its higher temperature because it does not have as much liquid water. When steam switches phase from a gas to a liquid, it releases a large amount of thermal energy (2202 kilojoules per kilogram at 121°C). The released thermal energy is directly transferred to the load items the steam touches, sterilizing them. As thermal energy is only transferred to load items steam touches, residual air within the sterilization chamber (i.e., the gas that is not water) will prevent steam from appropriately sterilizing all items within the autoclave. Thus, residual air is removed from the autoclave as part of the sterilization cycle. Saturated steam entering the chamber changes into liquid condensate as it contacts the colder surfaces of the autoclave chamber and loaded items. Also, retention of condensate (from gaseous steam converting into liquid) reduces sterilization cycle effectiveness. It is drained or vacuumed so that the condensate doesn’t become a barrier to the steam’s contact with items under the sterilization. A medical device’s steam sterilization cycle parameters depend on many factors, including the heat lability of the device materials, device heat penetration, and the medical device’s mass.
How is residual air removed from an autoclave?
Mechanically assisted pre-vacuum cycles or gravity displacement can remove air from an autoclave. Air is most effectively removed with pre-vacuum cycles utilizing multiple evacuation pressure pulses where the air is replaced by steam. Alternating vacuum and pressure pulses can stress the wrappings for items undergoing sterilization. Thus, evacuation pressure must be carefully selected for the autoclaves’ steam sterilization cycle. For pre-vacuum processes, the vacuum system removes residual steam and condensate from the sterilization chamber. Gravity displacement takes advantage of the heat and density of steam to remove air. In gravity displacement, the steam naturally rises to the top of the autoclave because it is hotter and less dense than air, while colder air exits from the bottom. Gravity displacement cycles remove condensation with the use of drains. Overall, autoclaving with a gravity displacement cycle will remove air much slower than systems with mechanically assisted air removal.
How do you calculate and control the lethality of an autoclave’s sterilization cycle?
Autoclaves are controlled by computerized systems that execute the sterilization cycle and report cycle data (e.g., temperature and pressure data at regular time points). Steam sterilization is monitored with calibrated temperature and pressure sensors. A method’s lethality target (F0) is the minimum time and temperature at which an autoclave must hold a cycle to ensure sterility. F0 determines sterilization time equivalency (in minutes). Traditionally, a base temperature of 121°C and a z-value of 10°C are used to determine F0 equivalency. The z-value is a measure of microbial resistance to sterilization based on a 10°C temperature change. However, temperatures other than 121°C can be used to calculate lethality equivalency. Autoclave cycle efficacy is measured using F0, as the F0 method measures standard sterilization equivalency for cycles operated at varying temperature conditions. The F0 minimum time is often set and calculated for each cycle after the initial residual air and condensate have been removed from the autoclave. Exceeding the minimum time-temperature requirements (F0) for a sterilization cycle is acceptable because the lethality level is exceeded. Also, there are minimal adverse effects to exceeding F0 requirements for the sterilized item materials.
The total accumulated F0 for of 121°C and a z-value of 10°C is determined by the following equation:
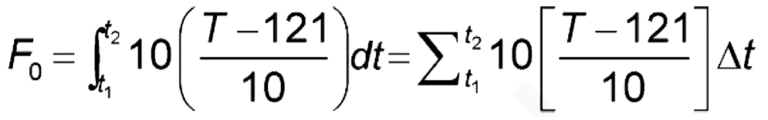
Where: t1 = start time; t2 = end time; T = temperature
Adding up the instantaneous lethality time and temperature contributions over the entire sterilization process will provide the F0 for the autoclave’s sterilization process. The F0 calculation should begin at 100°C and continue through the end of the saturated steam dwell period. F0 determination for the sterilization cycle should not count any instances where saturated steam is not maintained towards total F0 calculations.
Summary
Steam sterilization is the cheapest and the most ubiquitous sterilization method. Steam sterilization kills microbes through exposure to pressurized steam in sterilization chambers known as autoclaves. Since the sterility of a medical device or product is based on acceptance criteria, autoclave cycle sterility can be assured only by using a validated sterilization process (overkill method) under current good manufacturing practices (cGMP). An acceptable level of contamination risk for most items is probability of contamination for one in a million products. The lethality of an autoclave’s cycle is determined by a sterilization time equivalency value known as F0. All in all, ensure you choose a contract testing organization that can support you with appropriate sterilization validations and sterility testing for your unique medical device or product needs.
Ethide Labs is a contract testing organization specializing in Sterilization Validations and Sterility Testing. Ethide Labs also offers Bioburden Testing, Bacterial Endotoxin Testing, EO Residual Testing, Microbiology Testing, Cytotoxicity Testing, Environmental Monitoring & Package Integrity Testing services for medical device companies and allied industries. Ethide is an ISO 13485 certified facility.
References
United States Pharmacopeial Convention. <1229> Sterilization of Compendial Articles. Rockville, MD, USA. 2021. (USPC <1229>).
United States Pharmacopeial Convention. <1229.1> Steam Sterilization By Direct Contact. Rockville, MD, USA. 2021. (USPC <1229.1>).
Share this in your social networks


