Bioburden and USP 62
What does USP 62 Cover?
USP 62 covers tests for specific microorganisms. These assays quantify whether a specimen complies with the established quality specifications for microbiology. This guidance does not cover automated methods but states that automated methods may be used as long as they are equivalent to the tests outlined in this standard.
Procedures and Tests Covered in USP 62
For the tests described in USP 62, samples are to be prepared as detailed in USP 61. If the specimen being tested has antimicrobial activity, the antimicrobial activity must be neutralized before testing. If specimen sample preparation uses surface-active substances, compatibility and toxicity of the surface-active substances with the microorganisms under evaluation are verified.
Assays must be verified to establish that microorganisms in the presence of the product or specimen can be detected. Test strains of certain microorganisms (such as Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), Escherichia coli (E. coli), Candida albicans (C. albicans), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) are prepared for positive controls. When prepared these strains must not be more than five passages from the original master seed-lot. Negative controls are created using the diluent of the positive control test strain preparations. Appropriate negative controls will have no microbial growth when assays are performed.
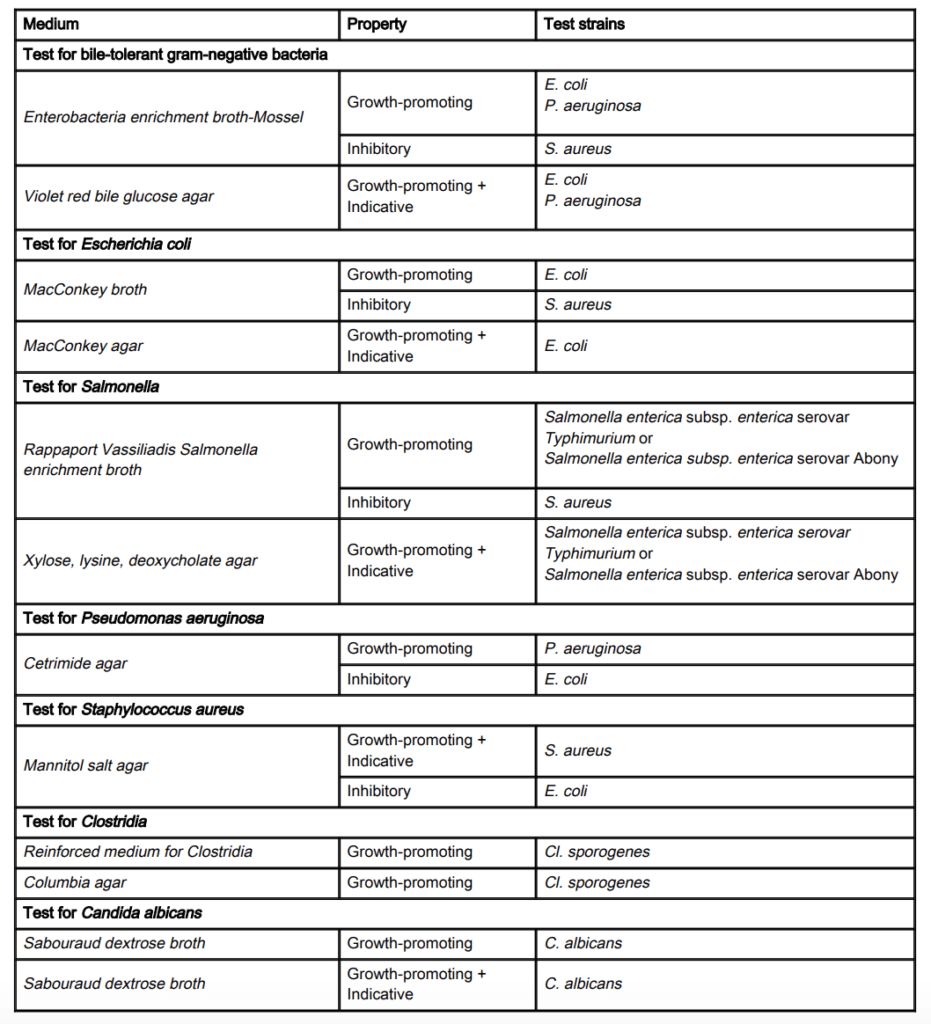
USP 62 contains the growth-promoting, inhibitory, and indicative properties of various media types for different microbial test strains in Table 1 of the document, which is reproduced below. Additionally, USP 62 describes test methods for assaying growth-promoting and inhibitory properties in both solid and liquid media along with microbial tests for indicative properties.
Testing of Products
USP 62 describes product tests for E. coli, Salmonella, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, Clostridia, and C. albicans. Tests are performed by adding not less than 1g or 1 ml of the product to be examined (following sample preparation instructions from USP 61). Exceptions to this are Clostridia, which requires not less than 2g or 2 ml, and Salmonella, which requires not less than 10g or 10 ml of the product to be examined. Samples are pre-incubated from 18-24 hours at 30-35°C. Samples are then transferred to an appropriate broth for the microorganism of interest and sub-cultured on agar with the appropriate nutrients for the microorganism of interest at 30-35°C for at least 18 hours. The product meets the standard if colonies of the microorganism assayed are not present or if confirmatory identification tests are negative.
Recipes for the following recommended solutions and culture media are detailed in USP 62:
- Phosphate buffer solution pH 7.2
- Sabouraud Dextrose Agar
- Soybean Casein Digest Broth
- Soybean Casein Digest Agar
- Buffered Sodium Chloride- Peptone Solution pH 7.0
- Potato Dextrose Agar
- Sabouraud Dextrose Broth
- Enterobacteria Enrichment Broth Mossel
- Violet Red Bile Glucose Agar
- MacConkey Broth
- MacConkey Agar
- Rappaport Vassiliadis Salmonella Enrichment Broth
- Xylose Lysine Deoxycholate Agar
- Cetrimide Agar
- Mannitol Salt Agar
- Reinforced Medium for Clostridia
- Columbia Agar
How do USP 61 and 62 relate to bioburden testing?
The “bio” in bioburden refers to live biological organisms and the “burden” in bioburden refers to the concentration of the viable biological organisms. The higher the concentration of viable organisms on a device or product, the higher the burden is to kill those organisms. The USP <62> pharmacopeia methods outline the specifics of how the microorganism testing for bioburden testing should be carried out. Specifically, USP <62> describes the preparation of test stains for aerobic microorganisms, various tests for microorganisms (E. coli, C. albicans, Salmonella, etc.), microorganism sample preparation for positive controls, and recipes for recommended solutions and culture media for the assays detailed in this guidance. When performing testing in-house or outsourcing your testing to a contract testing facility, it is important to make sure the USP <62> pharmacopeia methods are met for all bioburden testing. Additionally, bioburden testing should meet pharmacopeia methods from USP <60> and USP <61>.
Ethide Labs is a contract testing organization that specializes in Bioburden Testing. Ethide Labs also offers Bacterial Endotoxin Testing, Environmental Monitoring, Sterilization Validations, Microbiology Testing, EO Residual Testing, Package Integrity Testing & Cytotoxicity Testing services for medical device companies and allied industries. Ethide is an ISO 13485 certified facility.
References
United States Pharmacopeial Convention. <62> Microbiological Examination Of Nonsterile Products: Tests For Specified Microorganisms. Rockville, MD, USA. 2021. (USP <62>)
The link here will take you to the 2016 edition of USP <62>
Share this in your social networks