Sterility Testing Methods For Regulatory Testing
What is sterility?
The term sterile means a complete absence of viable microorganisms or microbes that have the potential to reproduce. Thus, sterile products are often chemically or heat sterilized after being placed in their final packaging. The chemical or heat sterilization kills any microorganisms inside the products (obtained during manufacturing and packaging). This chemical or heat sterilization process after final product packaging is known as terminal sterilization.
What are sterility testing and sterilization validations?
Sterility testing evaluates a product for live microbes. It ensures that microbes have been appropriately excluded from a product through aseptic processing or that microbes have been effectively killed through a terminal sterilization method. Sterility tests are performed at time zero (immediately after manufacture) and after stability testing for a period (such as 6 months or a year). Sterilization validations validate sterilization processes. For terminal sterilization processes, sterilization validations confirm that a certain threshold of microbial death occurs and occurs consistently.
What test methods are used for sterility testing?
The USP and EP sterility tests specify two basic methods for performing sterility tests; direct transfer (also known as direct inoculation) and membrane filtration methods. In some cases, the membrane filtration method may be the only choice for sterility testing.
Direct Transfer Method
The direct transfer (DT) method is the most traditional sterility-test method performed on samples from recently sterilized batches of products.
The direct transfer method involves five steps:
- Aseptically opening each sample container.
- Using a sterile syringe and needle to withdraw the required sample volume from the container.
- Injecting one-half of the required sample volume into a test tube containing FTM.
- Injecting the other half of the sample volume into a second test tube containing TSB.
- Mixing the sample and the culture medium for FTM and TSB-filled test tubes maximizes the interaction between the microbes and the culture medium to encourage microbial growth.
The DT method is simple on paper but difficult in practice. Those performing the DT test must have excellent physical dexterity and excellent skills at maintaining asepsis moment-to-moment when testing the sterility of multiple containers. Moment-to-moment maintenance of asepsis is particularly important due to the repetition in opening containers, sampling, transferring, and mixing, which can cause fatigue and boredom. As fatigue and boredom occur, the risk of accidental product sterility-test contamination increases.
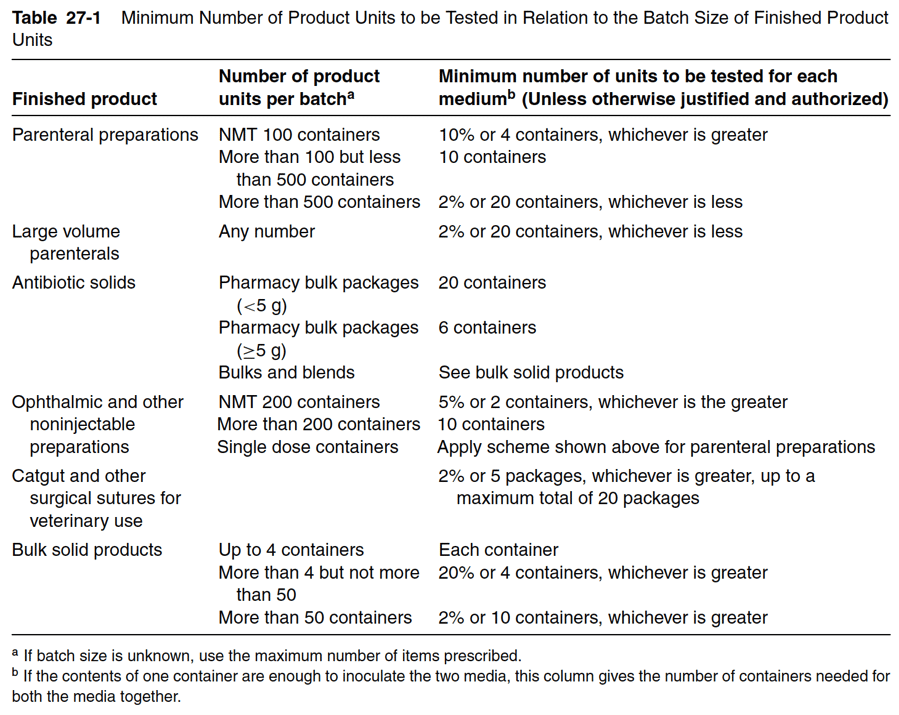
The USP and EP sterility testing guidelines require a minimum sample volume per container to be transferred. Indeed, the USP and EP want to ensure that the sample volume is sufficiently representative of the entire container volume being tested and will identify any present microbial growth. Minimum sample volumes to be transferred and the amount of media needed to culture that sample volume is given in Table 27-1 below.
Membrane Filtration Method
The membrane filtration (MF) sterility test became an official test method for sterility in 1970. Since then, MF is the most popular and widely used sterility test method, compared to the DT method. Though the MF methods require more technical skill and knowledge than the DT methods, the MF method offers advantages over the DT method. These advantages are described in detail below.
The membrane filtration sterility-test method has five steps:
- The filter unit must be properly sterilized and assembled before use.
- The contents of the sample units to be tested are transferred to the filter assembly under aseptic conditions.
- The contents are filtered with the aid of a vacuum or pressure differential system.
- The appropriate type and volume of culture media are added to the canister.
- The canister is incubated according to the medium used.
Membrane filter units consist of an assembly that facilitates the aseptic handling of the test solution and allows the membrane to be removed aseptically for transfer to an appropriate sterile media for incubation. In some cases, membrane filters are transferred to another assembly where sterile media can be added to the sealed filter and the membrane incubated in situ. A membrane for sterility testing has a rating of 0.45 m, and a diameter of approximately 47 millimeters. Membranes for sterility testing must have hydrophobic edges or low product-binding characteristics to minimize the collection of product residue. The collection of product residues must be avoided since product residue interferes with bacteriostasis and fungistasis testing.
How do direct transfer and membrane filtration methods for sterility testing compare?
The membrane filtration method offers at least four advantages over the direct transfer method. First of all, the membrane filtration method offers testing greater sensitivity. Secondly, when performing the membrane filtration method, the antimicrobial agent (s) and other antimicrobial solutes in the product sample can be eliminated for sterility testing with a rinse step prior to transferring the filter into test tubes of media. This rinsing step minimizes the incidence of false-negative test results. In contrast, the direct transfer method does not allow for the simple elimination of antimicrobial agents and solutes. The third advantage of the membrane filtration method is the entire contents of sample containers can be tested instead of a small representative volume of the container. The testing of the entire sample container is particularly advantageous when testing the sterility of large-volume parenteral products. Indeed, small contamination from large-volume parenteral products can be concentrated and detected on the membrane by filtering large volumes of product. Additionally, membrane filtration results are faster since testing only requires a seven-day incubation.
How do you interpret sterility test results?
After either the direct transfer or membrane filtration methods, there must be no visible evidence of microbial growth in a culture medium test tube after incubation. A lack of microbial growth is representative of the absence of contamination within the samples. Microbial growth in samples from sterility tests should be assessed by those trained in microbiology who know about industrial sterilization methods (and their limitations), aseptic processing, statistical concepts involved in sampling lots, and environmental control procedures used in the testing facility.
If microbial growth is found, or if the sterility test is determined to be invalid due to inadequate environmental conditions, the sterility test is then repeated. If microbial growth is found, facilities should thoroughly investigate their aseptic processes, non-sterile process thresholds, and terminal sterilization process to ensure contamination does not occur for future batches.

Summary
Overall, the USP and EP sterility tests are performed via a direct transfer method or a membrane filtration method. The membrane filtration method is faster, preferred for large-volume parenteral products, and is the only choice for sterility testing of some products. After either the direct transfer or membrane filtration methods, a lack of microbial growth represents the absence of contamination within the samples. An absence of contamination confirms the sterility of the product. When outsourcing testing for your medical products, ensure you choose a contract testing organization that can support you with appropriate sterility testing for your unique medical device, parenteral product, or medical product needs.
Ethide Labs is a contract testing organization that specializes in Sterilization Validations and Microbiology Testing. Ethide Labs provides in-vitro cytotoxicity tests in-house and outsources in-vivo cytotoxicity work for toxicity testing of medical devices, products, and drugs. Ethide Labs also offers Environmental Monitoring, Bioburden Testing, Bacterial Endotoxin Testing, EO Residual Testing, Package Integrity Testing & Cytotoxicity Testing services for medical device companies and allied industries. Ethide is an ISO 13485 certified facility.
References
Michael J. Akers. Sterile Drug Products Formulation, Packaging, Manufacture, and Quality. Drugs and the Pharmaceutical Sciences. Informa Healthcare. 2010.
Share this in your social networks


