Sampling For Sterility Testing
What is sterility?
The term sterile means a complete absence of viable microorganisms or microbes that have the potential to reproduce. Thus, sterile products are often chemically or heat sterilized after being placed in their final packaging. The chemical or heat sterilization kills any microorganisms inside the products (obtained during manufacturing and packaging). This chemical or heat sterilization process after final product packaging is known as terminal sterilization.
How is sampling for sterility testing performed?
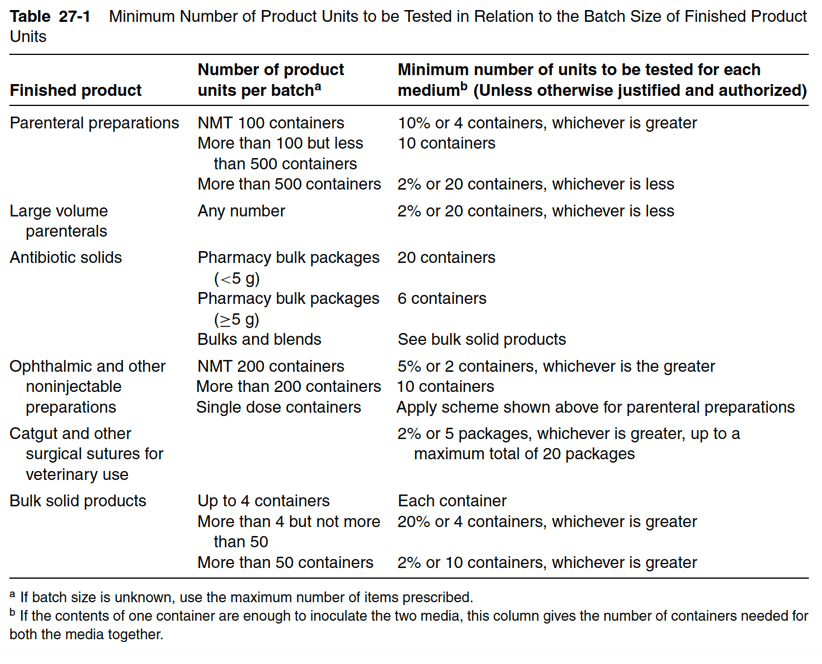
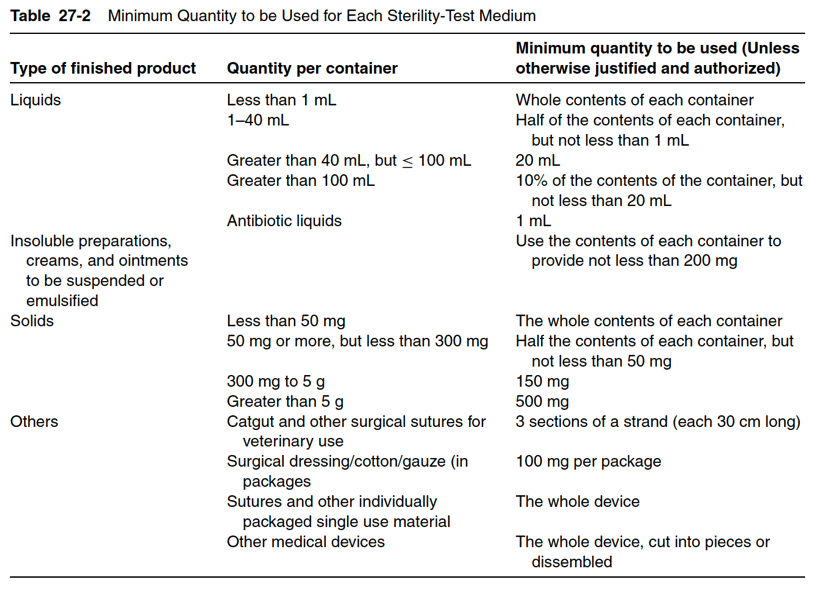
The number of sterile, packaged units sampled for sterility depends on the number of units in the batch, the volume of liquid per container, the method of sterilization, and the proper manufacturing practice requirements of the regulatory agency for the product. Most product manufacturers will sterility test 10 to 20 units of product per lot. If the medical product volume is one milliliter or less, the medical product may double the number of units tested. To give some examples, if the batch size is greater than 500 units, a minimum of 20 units will be tested. If the final batch size is between 100 and 500 units, then at least 10 articles are sterility tested. Note that for biologics, the minimum requirements for sterility testing differ. For large-volume products with a volume of 100 milliliters per container or more, at least 2% of the batch or 10 containers (whichever is less) are tested. Table 27-1 below provides the number of units to be sterility tested based on batch size. Table 27-2 shows the requirements for the minimum quantity of product to be used in the sterility test based on quantity per container.
What is needed for sterility testing sampling?
Culture Media For Sterility Testing
Three primary types of culture media are used in the sterility testing of injectables and other medical products: fluid thioglycollate medium (FTM), soybean-casein digest (SCD), and trypticase soy broth (TSB). FTM provides a healthy environment for both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria, with its primary intention being the culture of anaerobic bacteria. The thioglycollate and L-cysteine are antioxidants that maintain the anaerobic environment in culture. FTM solution has a two-color appearance, and the pink color at the top part of the solution should consume no more than one-third of the medium volume when in culture. Devices containing tubes with small lumens are sterility tested using a thioglycollate medium in which the agar and resazurin sodium are removed. The same modified thioglycollate medium is used for turbid or viscous injectable products. Agar removal allows for the media to fill small lumens easily. For oily products, Polysorbate 80 is added to FTM. Polysorbate 80 acts as an emulsifying agent between the oily product and medium and supports accurate stability testing. Soybean-casein digest (SCD) and trypticase soy broth (TSB) medium are used interchangeably. TSB has a slightly higher pH (7.3) than FTM (7.1) and is a better nutrient for the growth of fungal contaminants. Also, TSB is a better medium for slow-growing aerobic microorganisms than FTM.
After all culture media preparations, a validated steam sterilization process is applied to the medium. If media for stability tests are stored, the storage temperature is kept between 2◦C and 25◦C in sterile, airtight containers. When membrane filtration is used for the sterility test, a diluting fluid is used to rinse the filtration assembly to ensure that no microbial cells remain anywhere except the filter surface. It is imperative to use a diluting fluid for rinsing as it minimizes the destruction of small populations of cells during the pooling, solubilizing, and filtering of sterile products.
Incubation Time & Temperature For Sterility Testing
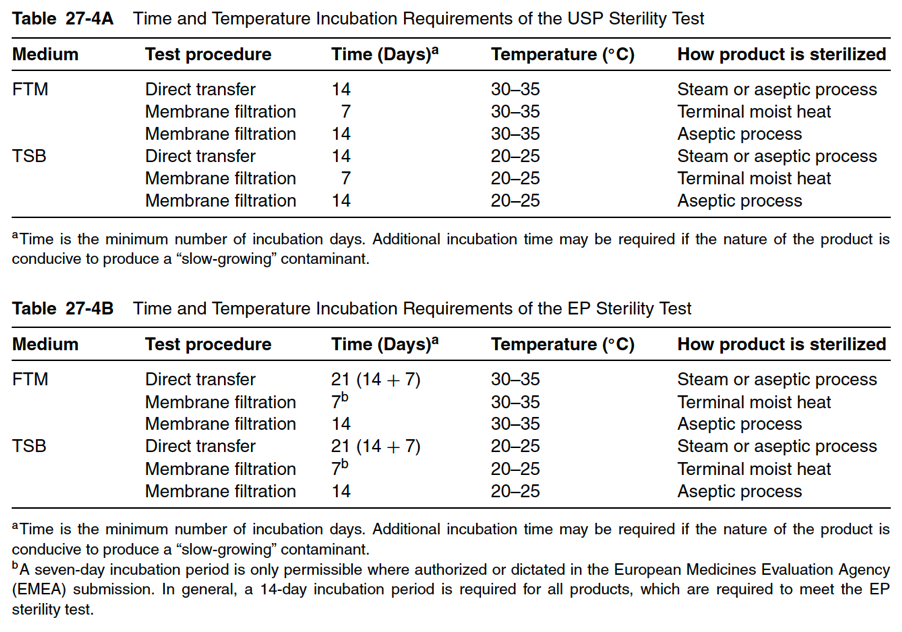
No ideal incubation time and temperature exist that caters to all microorganisms. Most organisms grow more rapidly at 37◦C. However, some organisms prefer to grow at 23◦C and resist growth at higher temperatures. For example, a pseudomonad contaminant in plasma grew in FTM at 25◦C but was killed at 35◦C. The current time and temperature incubation requirements of the USP and EP sterility tests are found in Tables 27-4A and 27-4B below. Generally, incubations in TSB are at 20◦C to 25◦C because this temperature range is favorable for the growth of fungal and slow-growing aerobic contaminants. The incubation time for sterility testing by membrane filtration is 14 days and an additional four days to detect microbial growth in the media used as negative controls (after adding a challenge organism).
Sterility test methods
The USP and EP sterility tests specify two basic methods for performing sterility tests the direct transfer (also known as direct inoculation) method and the membrane filtration method. In some cases, the membrane filtration method may be the only choice for sterility testing.
Summary
Overall, the number of samples required for stability testing varies based on the size of the batch and the volume of the product. To perform stability tests, either an FTM, TSB, or SCD media is used to incubate and grow any microbial contaminants. Temperatures for stability testing vary based on the media used and stability test method. All in all, when selecting a contract testing organization, ensure you choose one that can support you with selecting appropriate stability testing for your unique medical device or product needs.
Ethide Labs is a contract testing organization that specializes in Sterilization Validations. Ethide Labs provides in-vitro cytotoxicity tests in-house and outsources in-vivo cytotoxicity work for toxicity testing of medical devices, products, and drugs. Ethide Labs also offers Bioburden Testing, Environmental Monitoring, Microbiology Testing, Bacterial Endotoxin Testing, EO Residual Testing, Package Integrity Testing & Cytotoxicity Testing services for medical device companies and allied industries. Ethide is an ISO 13485 certified facility.
References
Michael J. Akers. Sterile Drug Products Formulation, Packaging, Manufacture, and Quality. Drugs and the Pharmaceutical Sciences. Informa Healthcare. 2010.
Share this in your social networks


